BNP Paribas expanded its balance sheet by 23% (!) in the first quarter of 2020, as companies took out emergency loans in response to the coronavirus panic.
Sean Pawley talks about banking in East Africa on the Palladium Podcast (discussion about banks between 6:50 and 22:15). Multiple issues with banking in Rwanda and other countries in the region: economy runs on cash payments -> banks lack reliable data on borrowers -> high default rates -> unstable banks, high interest rates and fees, preference of cash over bank deposits. His solution: a narrow bank that eliminates credit risk. Provide a cellphone-based payment solution. Collect payment data. Based on the data, start making loans.
The KBC mobile banking app will show highlights of the Belgian football Pro League. This service is available to anyone who installs the app, including non-customers.
Climate change’s new ally: big finance discusses the role of asset managers in reducing emissions.
A model of the Eurozone architecture embedded in the global US dollar system by Steffen Murau (using the analytical framework of interlocking balance sheets!)
Facts and myths about bank leverage ratios (from 2014, but timeless). Dan Davies explains why reducing risk to a single metric cannot work.
More on the miracles of bank regulation:
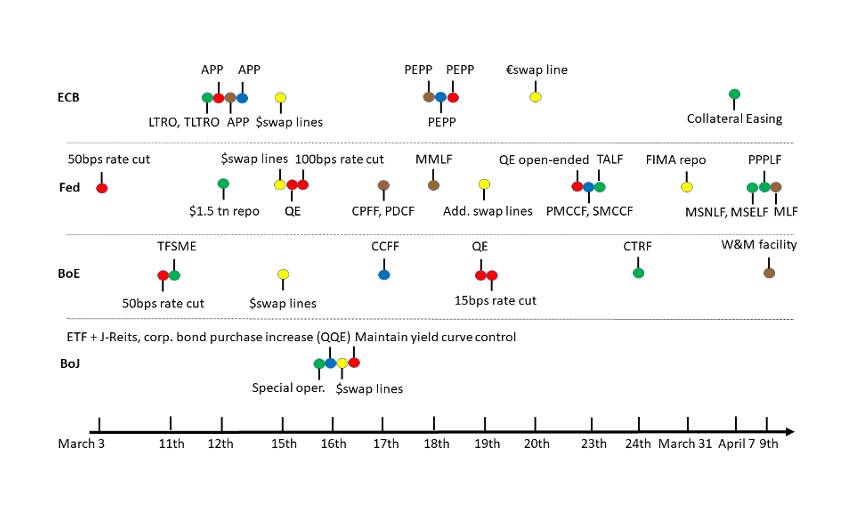
Revisiting the Ides of March: how banks’ liquidity rules complicated the corporate demand for cash during the coronavirus panic of March 2020.